Data can be classified in 3 groups.
- Structured data. ie. Any data structured in a data base
- Semi-structured data. ie. Any data coming from an XML document, since it can be partially stored into a data base.
- Unstructured data or BIG DATA. Data from social media sites, web logs etc… that cannot be stored analysed and processed in databases.
This means that the idea that you can extract from millions of Clinical health records processed together as BIG DATA relevant information is basically wrong, since a CHR is main a structured or semi-structured data furfilling standards and specific vocabularies into XML structures.
And although it is true that part of the information could be unstructure and processed as BIG DATA with tools such as HADOOP ecosystem, on the reality is that in most of the cases have to be processed as multimedia relational data bases.
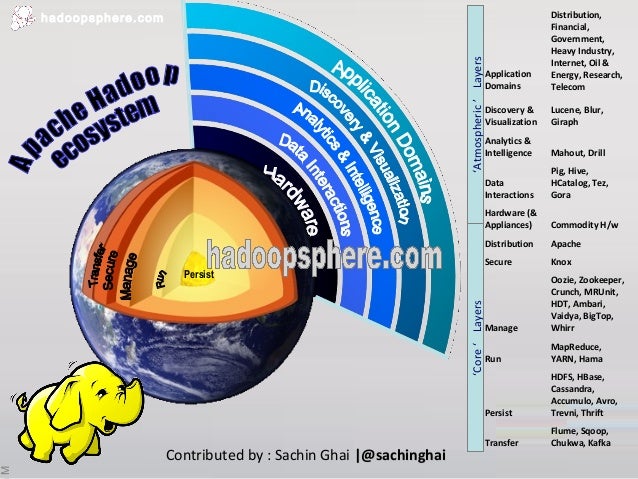
On this regard the essential tools of the big data processing systems such as:
- Distributed file systems (DFS): concentrate in several servers the data according to different criteria.
- Map reduce framework : reduce task take the output from the map task and reduce it into single key/value pair for each input.
- Stored values in column data bases: Obviously with a fast read acces.
- Access the data with a query tool similar to an SQL.
- Use distributed coordinated services, designed to run over a cluster of machines. Highly available services to manage operations and components.
- Redistributed data using a tool capable of moving data between relational daba bases and data warehouses.
- Dedicated service to collect, aggregate and move large amount of data from individual machines to the distributed file system.
InMemory processing in Spark.

