In the year 2000, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has solved the concerns about electromagnetic interference (EMI) from a variety of other licensed radio users (i.e emergency medical technicians or police) dedicating a portion of the radio spectrum: 608-614 MHz, 1395-1400 MHz and 1427-1432 MHz, for wireless medical telemetry devices.
WMTS (wireless medical telemetry services) was approved for any biomedical emission appropriate for communications, except voice and video. Transmitters operating in the WMTS bands had been registered with ASHE (American Society for Healthcare Engineering ) to ensure interference-free operation and notify users of potential frequency conflicts. At that time although some vendor supported 802.11 WIFI or Bluetooth, both the FCC and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) encourage the use of WMTS.
Since 2009 the 802.11n WIFI covered more then 76% of all wireless access point.
Medical WIFI in Hospitals became the main source for:
- Guest services
- Real time location
- Remote video access
- Support telemedicine
- Offer voice over wifi
- Accomodate Wireless medical devices
- Access EHR (electronical health records) and other healthcare applications
This was further increased with BYOD (bring your own device) phylosophy and FCC expected by 2013 to run out of spectrum that could seriously limited the QoS required in medical applications and roaming movility.
For that reason 802.11r appeared and solved this problem together with the micro-cells that provide a very dense WIFI networks. An furthermore the 802.11h amendment from IEEE assure that 4 GHz band do not interfere with radar stations. Finally the 802.11u ready by 2011 improved the internetworking and rooming.
Since 2012 the FCC reserved the MEDICAL PERSONAL AREA NETWORK and with Continua Health Alliance is providing wireless certification program for medical devices.
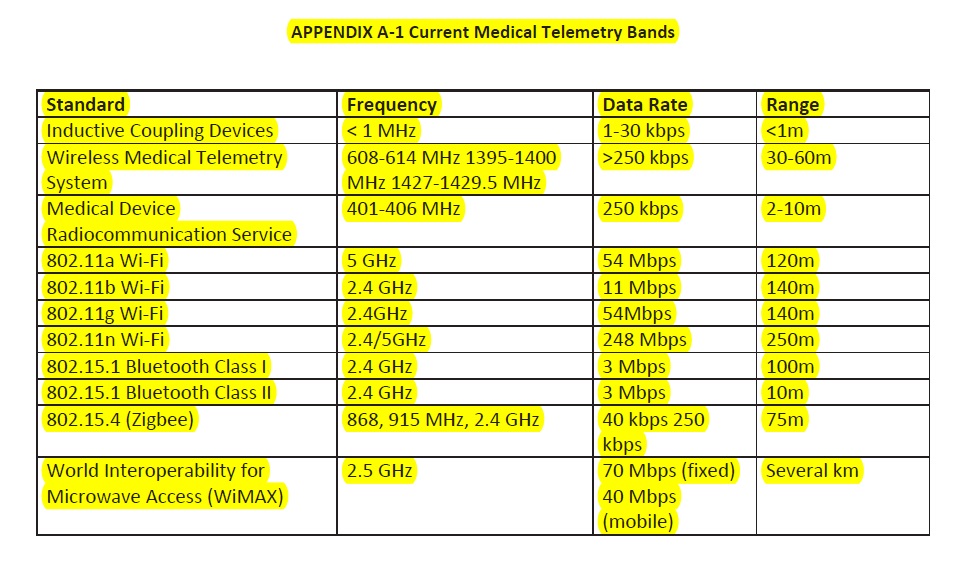
mHealth Alliance have defined since then mHealth as the medical and public health practice suported by mobile medical devices. At that point REGULATIONS IN THE NEW MEDICAL HEALTH essentially consider mHealth and the current medical telemetry bands were:
Low energy solutions for wearable sensors exploted at that time. Body Area Network is formally defined by IEEE 802.15 as, “a communication standard optimized for low power devices and operation on, in or around the human body (but not limited to humans) to serve a variety of applications including medical, consumer electronics / personal entertainment and other” [IEEE 802.15].
The WG6 specifications IEEE 802.15.6 also know as WBAN (wireless Body area network) was ready in 2012. It supports quality of service (QoS), extremely low power, and data rates up to 10 Mbps complying with strict non-interference guidelines. It supports a variety of frequency bands including 868-868.6 MHz, – 802-928 MHz, – 2400-2483.5 MHz, – 314-316 MHz, 430-434 MHz, and 779-787 MHz band for LR-WPAN systems in China, and – 950 MHz-956 MHz in Japan. The standard take into consideration body interactions of portable antennas (varying with male, female, skinny, heavy, etc.), radiation pattern shaping to minimize the specific absorption rate (SAR) into the body, and changes in characteristics as a result of the user motions.

IEEE 802 Working Groups and Study Groups
- 802.1 Higher Layer LAN Protocols Working Group
- 802.3 Ethernet Working Group
- 802.11 Wireless LAN Working Group
- 802.15 Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) Working Group
- 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group
- 802.18 Radio Regulatory TAG
- 802.19 Wireless Coexistence Working Group
- 802.21 Media Independent Handover Services Working Group
- 802.22 Wireless Regional Area Networks
- 802.24 Smart Grid TAG
- OmniRAN EC Study Group
- List of Hibernating and Disbanded Working Groups and Study Groups
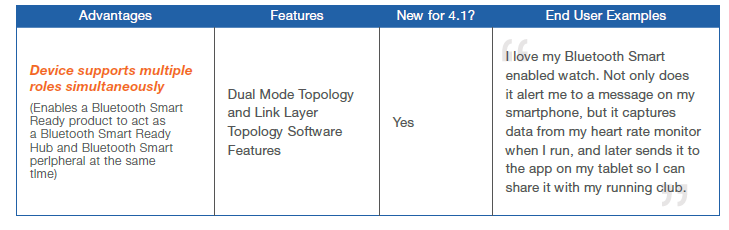
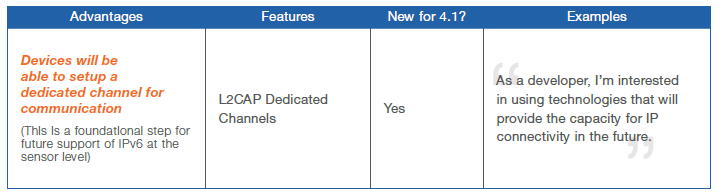
2013: The new Bluetooth Smart of low energy (v.4.0) – BLE is facing a new more versatile version (v.4.1) approved on Dicember 2013 that will be on the market by the end of 2014. It is a great improvement since it is more efficient with IoE and therefore supporting Health 4.0 since it is capable to behave as Hub and as peripheral and to have a dedicated channel. Now available in Microchip.