LoRaWAN low-power WAN technology standard is promoted by the France Telecoms (Orange) and Swiss telecoms (Swisscom) to create the strategy for Actility’s ThingPark open standard IoT network solution.
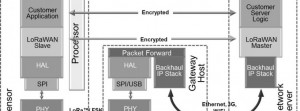
The ThingPark connect both long range and low power sensors over unlicensed ISM band spectrum with allows low-cost and fast roll-out networks.
The result: Operators capable to accelerate the connection of objects. The open standard will change IoT applications from “industrial based” for smart metering, remote monitoring and logistics applications towards “world wide based” for free individual user applications.
Bouygues has been trialling LoRa in Grenoble since 2013 and it is ready for a nationwide rollout this summer, and expects 500 towns and cities to be covered by the end of the year.
Competitors with similar strategies are: Vodafone – EMC in Ireland; Sigfox – Samsung with networks in Belgium (Engie) ; Weightless SIG – Nwave in London.
Here’s a list of IoT implemetations LoRa reckons its technology is good for:
- Smart Cities (smart parking, building surveillance, sound monitoring, people detection, traffic management, street lighting management, domestic waste management, billboard displays, etc.)
- Smart Environment (fire detection, air pollution, snowfall measurement, avalanche prevention, flood and drought monitoring, earthquake detection, etc.)
- Smart Water (drinking water monitoring, chemical contamination detection, swimming pool monitoring, seawater pollution measurement, leak detection, tide monitoring, etc.)
- Smart metering/smart Grid (smart electricity/water/gas meters, measurement of liquid levels, monitoring of photovoltaic installations, water flow, calculation of stock in silos, etc.)
- Tracking (vehicles, bicycles, objects of value, animals, people)
- Safety and Rescue services (analysis of presence in dangerous/forbidden zones, presence of dangerous liquids, radiation levels, detection of explosive substances, etc.)
- Commerce (supply chain control, mobile payments, smart shopping, shelf stock rotation)
- Logistics (monitoring of transport conditions, parcel localisation; detection of stock incompatibility, fleet traceability, etc.)
- Industrial monitoring (monitoring of machines/state of equipment, indoor air quality, temperature control, ozone level detection, localisation of equipment/products indoors, vehicle servicing, etc.)
- Smart Agriculture (monitoring of greenhouses and vineyards, golf course irrigation management, weather stations, compost, animal tracking, etc.)
- Smart Livestock Care (traceability of pasture feeding, monitoring of toxic gas levels, animal progress monitoring, hydroponic farming, etc.)
- Smart Buildings & Homes (water and electricity consumption, remote control, intruder detection, smoke detection, surveillance of valuables, etc.)
- eHealth (fall detection, medicine storage, sporting performance monitoring, patient monitoring, ultraviolet radiation, etc.)
Located in the last part of the list, eHealth is by far the first one. It is the main democratic deployment of IoT as the HUMANIZATION OF HEALTHCARE (H2O) consortium have proved to deploy Health 4.0.

